The Rise and Fall of Joseph McCarthy
This video tells the story of the rise and fall of Senator Joseph McCarthy, a fierce partisan and demagogue whose battles against Communism in early 1950s America utilized the new medium of television to garner public attention. Preying upon the public's fear of communism within the U.S. government, he hurled accusations against numerous political enemies often with little or no evidence, and with scant regard to the principles of due process, free speech, and liberty. The new medium of television, which helped his meteoric political rise, would ultimately play a key role in his undoing.

The Notorious Aaron Burr
You may know him as the man who killed Alexander Hamilton, but do you know the full story of one of American History's most notorious characters? Our latest Homework Help Institute of History video brings you the story of Aaron Burr, his rise to the position of governor of New York and vice president of the United States, and his spectacular downfall.

African Americans in the Gilded Age
This video provides a general overview of the experience of African Americans during the pivotal years of the Gilded Age, from the 1860s to the early 1900s. Despite the passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution after the Civil War, which abolished slavery and granted citizenship and voting rights to African American men, millions of African Americans across the nation still faced an uphill struggle for equality and civil rights. Political disenfranchisement was widespread and segregation in the form of "Jim Crow" laws affected nearly every facet of public and private life in the South. Many African Americans migrated from the South to the North and West during this period. This era also saw the rise of dozens of notable African American civil rights leaders including Ida B. Wells, Frederick Douglass, Booker T. Washington, and W.E.B. Du Bois. Groups like the N.A.A.C.P. were also established during this period to fight for the expansion of liberty and equality for African Americans.

Entrepreneurs: A History
This video focuses on the so-called "Robber Barons" or "Captains of Industry" of the late 19th and early 20th century, including Andrew Carnegie, John D. Rockefeller, J.P. Morgan, and Henry Ford. How did these men and those like them transform the U.S. economy during the Gilded Age, and what, if any, lessons do their stories have for us today?

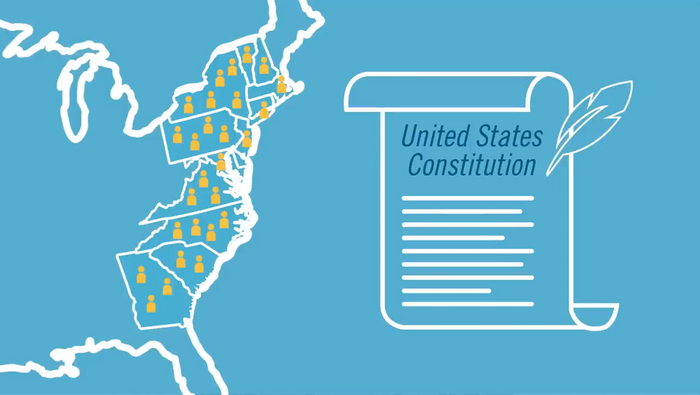
The Origins of Partisanship
This video addresses the origins of partisanship in the United States. In the late 18th Century, the new nation was at risk of being torn apart as factions developed between Federalists and Anti-Federalists whose differences over the nature and structure of the new government played out in pamphlets, newspaper essays, state ratifying conventions, in taverns, and on street corners. Some compromise was reached with the ratification of The Bill of Rights, but differences over policy continued to play out among factions and the Federalists and Democratic-Republican parties formed. This video is intended as a general overview of this period of U.S. History, and a springboard for a deeper exploration of the various political disputes of the late 1700s and early 1800s.

The Story of "Boss" Tweed
This video tells the story of William "Boss" Tweed. Tracing his rise to political power in post Civil War New York City, a metropolis whose population was booming from an influx of European immigrants, this video explores the question of whether Tweed was a hero, a villain, or something in between.
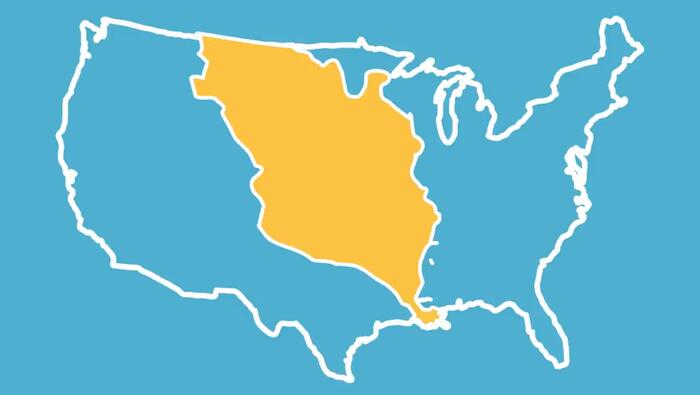
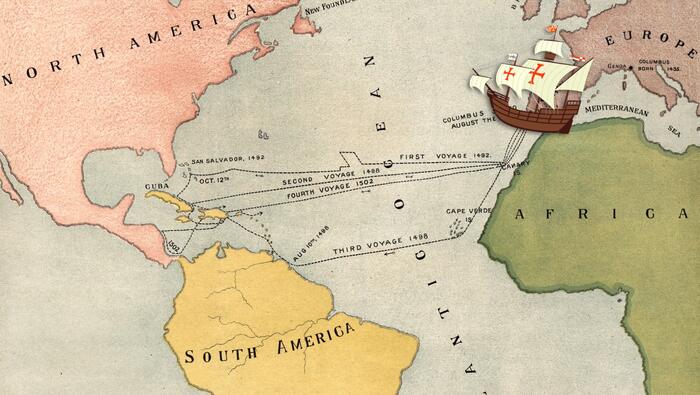
The Columbian Exchange
Have you ever looked at your teacher with a puzzled face when they explain history? I know we have. In our new Homework Help Series we break down history into easy to understand 5 minute videos to support a better understanding of American History. In our first episode, we tackle the Columbian Exchange and early contact between Europeans, Natives and Africans.

Dred Scott v. Sandford
The Dred Scott v Sandford case of 1857 was brought to the Supreme Court just four years before the start of the Civil War. Dred Scott sued his master for his freedom and Judge Robert Taney ultimately ruled two things in the Dred Scott decision. First, African Americans were not citizens and had no right to sue in court. Second, Congress did not have the constitutional authority to ban slavery from the states. This case is considered one of the worst rulings in the history of the Supreme Court.

Miranda v. Arizona
Miranda v Arizona was a case brought to the Supreme Court in 1966 after Ernesto Miranda appealed his guilty conviction of kidnapping and rape. In his appeal, Miranda claimed he was unaware of his right to remain silent, and his resulting confession should not be used to incriminate him. The Supreme Court ruled in favor of Miranda and established the Miranda Warning, otherwise known as Miranda Rights. This warning is now recited in most instances of arrest to ensure the accused people are aware of their rights.

Grutter v. Bollinger
Grutter v. Bollinger was a case brought to the Supreme Court over the use of Affirmative Action in the college admissions process. The University of Michigan Law School denied acceptance to Barbara Grutter, despite her impressive resume. Grutter, a white woman, believed that her rejection was based on her race. The Supreme Court Justices ultimately ruled that the University of Michigan Law School’s admissions process was constitutional and did not violate the Equal Protection Clause in the 14th Amendment. Incorporation, the process of states being held liable to the Bill of Rights, allowed the Supreme Court to hear and rule on the case.
However, there was doubt among the most conservative Supreme Court justices like Scalia and Rehnquist that affirmative action policy was a constitutional practice for university admission departments to take part in. Affirmative Action is still a highly debated topic today.

Regents of the University of California v. Bakke
Regents of the University of California v. Bakke was a case brought to the Supreme Court over the use of Affirmative Action in the college admission process. The University of California at Davis Medical School created a minimum minority student quota for the admissions department to fill each year. Bakke, a two-time UC-Davis Med School rejected applicant, sued the school for violation of the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment and Title VI of the Civil Rights Acts. Ultimately, the Supreme Court justices ruled in support of the goals of Affirmative Action because of incorporation, the idea that the states must adhere to the protections of the Bill of Rights. They also stated that Bakke was, in fact, denied equal protection. This decision, because it was so muddled, did not set long-term precedents or clarifications concerning Affirmative Action.
What is Affirmative Action? Affirmative Action is a policy, usually carried out by schools, businesses, government entities, and federal contractors, in which individuals of minority racial status are afforded preferential treatment on the basis of race. Affirmative action came about as part of a desire to rectify the traditional underrepresentation of minority peoples in desirable professions and universities, which negatively impacted their financial and social conditions.
Citizens United v. FEC
Citizens United v. FEC was a Supreme Court case surrounding campaign finance and corporate involvement in politics. The Federal Election Commission was created in 1971 and greatly regulated the amount of campaign finance political candidates were able to receive. By 2002, the Bipartisan Campaign Finance Reform Act (McCain-Feingold Act) restricted organizations from financing issue-based advertisements on behalf of candidates. This Citizens United v FEC summary explains how Citizens United released a million dollar ad against Hillary Clinton. Before the film aired, Citizens United challenged the McCain-Feingold Act, stating that money was a form of Free Speech, which is protected by the First Amendment. The Supreme Court ruled the McCain-Feingold Act as unconstitutional, but stated that corporations still cannot give money directly to political candidates.
Gibbons v. Ogden
Gibbons v Ogden was a Supreme Court case dealing with interstate commerce. Learn about Aaron Ogden, who in 1824 received a monopoly over steamboat access to the Hudson River thanks to a newly created New York law in this Gibbons v Ogden summary. On the other hand, Thomas Gibbons held a federal license to operate his steamboat between New York and New Jersey. Gibbons won unanimously through his connection of the Interstate Commerce Clause and Supremacy Clause. New York’s law was overturned and Gibbons, along with other steamboat operators were able to participate in Interstate Commerce via waterways.

Schenck v. United States
Schenck v. United States was a Supreme Court Case that explained some limits to the Freedom of Speech afforded by the First Amendment. During World War I, the US instituted a military draft. Many people released anti-war and anti-government information due to their displeasure with the draft. Charles Schenck, an anti-war socialist, was arrested by the Federal Government for circulating a pamphlet encouraging men to resist the draft and violating the Espionage Act of 1917. The Supreme Court ruled that wartime circumstances changed the rules related to free speech and resulted in the “Clear and Present Danger” rule.
McCulloch v. Maryland
McCulloch v Maryland was the 1819 Supreme Court case dealing mostly with the issue of Federalism. This McCulloch v Maryland summary explains the creation of a National Bank which was encouraged by Alexander Hamilton, but opposed by Thomas Jefferson, due to lack of authority given by the Constitution. The first National Bank was chartered, but then died 20 years later. In 1816, a National Bank was re-instated to help deal with debts from the War of 1812. This Second National Bank, established in Maryland, was taxed heavily by Thomas Jefferson and the State of Maryland. Federal Bank Cashier, James McCulloch, refused to pay the tax, stating that the state did not have the right to tax an institution of the Federal Government. Ultimately, the Supreme Court stated that Congress had the right to create the National Bank, under the Necessary and Proper Clause. Also, the State of Maryland did not have the right to tax the National Bank and the Federal Government under the Supremacy Clause.

Brown v. Board of Education
Brown v Board of Education was a case brought to the Supreme Court in 1954 after Linda Brown, an African American student in Kansas, was denied access to the white-only schools nearby her house. Future Supreme Court Justice Thurgood Marshall was the lawyer for the case, and argued that segregated schools were inherently unequal. Ultimately, the Supreme Court ruled in favor of Linda Brown and declared segregation unconstitutional under the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment through incorporation under the premise that the bill of rights also applies to the states. This is one of the landmark cases that led to the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
Marbury v. Madison
This Marbury vs Madison summary video displays William Marbury as a judge appointed at the end of John Adams’ presidency but who never got his official commission papers. Once Thomas Jefferson became president, James Madison refused to deliver the commission papers. Marbury took his case to the Supreme Court and wanted a Writ of Mandamus, requiring Madison to deliver the papers. Ultimately, the court stated that Marbury was entitled to his papers, but it was unconstitutional for the courts to issue a Writ of Mandamus. Thus, judicial review was created, and the principle of checks and balances was strengthened through Marbury vs Madison.

Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are essential gifts from nature, including food, clean air, water, and more. These services benefit both humans and all life on Earth. For instance, bees' pollination aids food growth, while wetlands store carbon and purify water. Protecting nature safeguards these vital services for our well-being and survival.

West Virginia State Board of Education v. Barnette
Should students be required to salute the flag? In 1943, the Supreme Court heard a case after Jehovah's Witnesses in West Virginia refused to comply with a school board policy requiring they salute the U.S. flag during the Pledge of Allegiance. How did the Court rule? Find out with our latest Homework Help video!

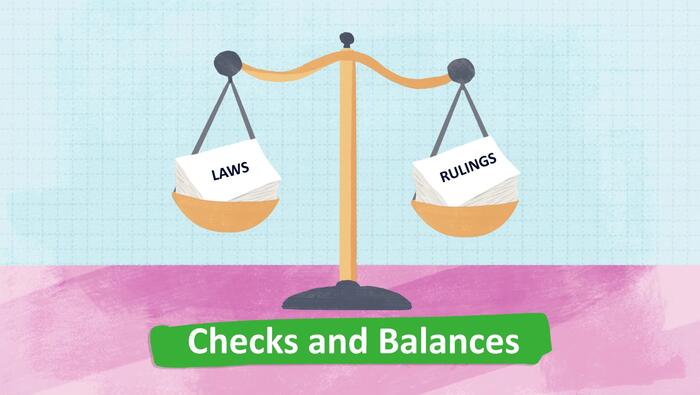
United States v. Nixon
Can the President of the United States withhold certain information from Congress and the courts? During the Watergate Scandal, President Richard Nixon attempted to withhold recording tapes from the White House from investigators. The Supreme Court’s ruling would have huge impacts on the system of checks and balances within the United States' governing system.

The Third Amendment
Why did the Founders believe so strongly that troops should not be quartered in the homes of citizens that they enshrined this protection in the Bill of Rights? The Third Amendment is rarely talked about, but studying its origins and purposes is important in order to understand our system of the relationship between civilians and the military. Learn more about the story of the Third Amendment with this Homework Help video.
The Second Amendment
What are the origins of the Second Amendment, and how has it been interpreted throughout U.S. history? This Homework Help video explores the history of the Second Amendment as well as the Supreme Court interpretations of it that shape current discussions on the topic of gun control.

The Fourth Amendment
What prevents the police from randomly searching our homes and possessions whenever they want? The Founders created the Fourth Amendment to protect the individual right to private property. Learn more about its origins and some landmark Supreme Court cases in our latest Homework Help video.

The Fifth Amendment
What protections does the Fifth Amendment provide, and why did the Founders believe those were important enough to enshrine in the Bill of Rights? Our latest Homework Help video explores these questions and provides students with a succinct overview of the essential information regarding this amendment.

Shaw v Reno
Can a state draw district lines to increase the voting power of a minority? The Supreme Court took up this question in the 1993 case of Shaw v. Reno. Following the 1962 Baker v. Carr Supreme Court case, which ruled that the Supreme Court could hear cases on gerrymandering because of the Equal Protection Clause in the 14th Amendment through the process of incorporation, Shaw v. Reno challenged the constitutionality of gerrymandering based on race.

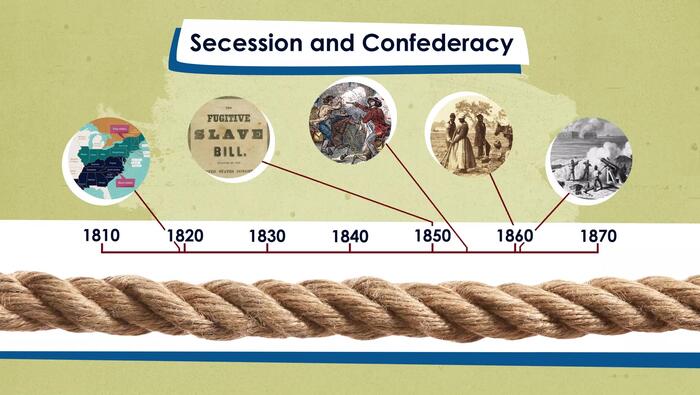
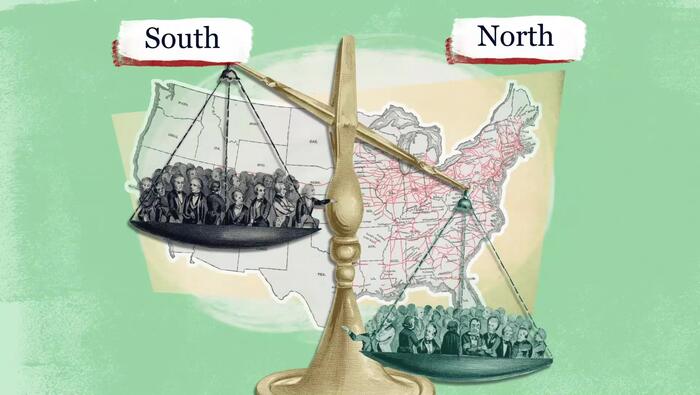
Reconstruction
How did the United States attempt to reunite after the Civil War while also securing the rights of recently freed enslaved people and how successful was our country in accomplishing these goals? Our latest Homework Help video explores these questions while encouraging students to analyze the Reconstruction period and its relationship with the principles of liberty and equality.

Kelo v. New London
Under what circumstances can the government take your property? In 2005, the Supreme Court took on this question in the case of Kelo v. New London. The court argued about whether applying the 5th Amendment to the states using the Due Process Clause of the 14th Amendment was constitutional or unconstitutional. This process is referred to as incorporation. Our latest Homework Help video reviews the details of the case and encourages students to analyze the decision to form their own opinions.

Free Assembly
Why is the freedom of assembly an essential right in a free society? Our Homework Help video explores why the Founders included it in the 1st Amendment as well as the landmark Supreme Court cases involving it. Supreme Court cases arguing freedom of assembly debate the protections of the 14th Amendment. Although the Bill of Rights was initially limited to the federal government, incorporation also allows states to be culpable of the protections in the Bill of Rights.

Engel v. Vitale
Is school-sponsored prayer in public schools a violation of the establishment clause of the First Amendment? In 1951, some New York schools began starting the day with a non-denominational prayer. Our latest Homework Help video tells the story of the ensuing landmark Supreme Court case of Engel v. Vitale.

Wisconsin v. Yoder
Religious liberty is one of the foundational principles of American society, but how should it be balanced with government interests in an educated citizenry? Our second Homework Help video of the semester is on the landmark case of Wisconsin v. Yoder, and how the Supreme Court dealt with this important question.

Freedom of the Press
What do you think of when you hear the words "free press"? The Founders believed the freedom of the press to be an important bulwark in a free society. Learn more about the history of the First Amendment as well as some landmark Supreme Court cases involving press freedom with this Homework Help video.

Bush v. Gore
Why was the presidential election of 2000 so controversial, and what constitutional questions were raised during the vote count? Our first Homework Help video of the semester explores these questions and will help your students understand the fundamental issues at hand in the case of Bush v. Gore!

The Story of Women's Suffrage in America (Part 2)
In part two of this two-part Homework Help narrative, learn about the challenges that the women’s suffrage movement overcame in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. What contributions did monumental suffragists like Alice Paul, Lucy Stone, and Carrie Chapman Catt make on the journey to winning the vote for women?

The Story of Women's Rights in Early America (Part 1)
In part one of this two-part Homework Help narrative, learn about the origins of the women’s suffrage movement from Colonial America through the nineteenth century. What challenges did these brave activists need to overcome in the early days of the movement to lay the groundwork for the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment?

Tinker v. Des Moines
Why did a subtle act of protest against a foreign war reach the Supreme Court? In 1965, students John and Mary Beth Tinker wore black armbands to school to protest the United States’ involvement in the Vietnam War, despite the Des Moines school district prohibiting such an act. The Tinkers sued the district for violating their First Amendment rights, and the Supreme Court ruled in their favor in a 7-2 decision. While subsequent Supreme Court rulings narrowed the scope of free expression rights at school, Tinker v. Des Moines remains a landmark case that has defined First Amendment rights for students.

Roe v. Wade
Do women have a right to privacy when deciding whether to have an abortion? In 1969, a woman under the alias “Jane Roe” challenged a Texas law that outlawed abortions. The case eventually reached the Supreme Court, where Roe argued that a woman’s right to privacy in having an abortion is protected by the Constitution. In a 7-2 decision, the Court ruled the right to an abortion fell within the right to privacy protected by the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause. To this day, the ruling in Roe v. Wade remains one of the most controversial Supreme Court decisions.

McDonald v. Chicago
Does the Second Amendment prevent a city from effectively outlawing handgun ownership? In 2008, Otis McDonald attempted to purchase a handgun for self-defense purposes in a Chicago suburb. However, the city of Chicago had banned handgun ownership in 1982 when it passed a law that prevented issuing handgun registrations. McDonald argued this law violated the Fourteenth Amendment’s Privileges and Immunities Clause as well as the Due Process Clause. In a 5-4 decision, the Court ruled that McDonald’s Second Amendment right to bear arms was protected at the state and local level by the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.

Gideon v. Wainwright
Does an individual have a right to a lawyer, regardless of the crime he or she is charged with? In 1961, Clarence Gideon was arrested and charged with breaking and entering and petty larceny in Panama City, Florida. His request for a state-provided defense attorney was denied since Florida law only required doing so for capital offense cases. After Gideon was sentenced to 5 years in prison, he argued that Florida violated the Sixth Amendment’s guarantee of the right to counsel. The Supreme Court heard Gideon’s case and ruled in a 9-0 decision that the Sixth Amendment’s guarantee of an attorney applies to states through the Due Process Clause of the 14th Amendment.

The Lost Generation
The devastation and disillusionment that resonated through society in the aftermath of World War I had a profound impact on the literary landscape, notably a group of U.S. writers living in Europe, including Ernest Hemingway and F. Scott Fitzgerald. These writers are known as the Lost Generation.

Victorian Literature
Exploring the diversity of Victorian Literature, we discover how authors like Charles Dickens, the Brontë Sisters and Lewis Carroll captured the ideals and issues of a rapidly industrializing society, weaving tales of innovation, societal norms and adventure in 19th Century England.

Transcendentalism
Transcendentalism is a spiritual, philosophical and literary movement that emerged in the United States in the 19th century. With its emphasis on individualism and the inherent goodness of all people, discover how it impacted civil rights movements via works by Louisa May Alcott, Henry David Thoreau and others.

Coming of Age
Coming of age stories chart a character’s journey from childhood through adolescence and into adulthood. This genre is also known by the German word, 'Bildungsroman'. We take a look at some classics of the genre, from Charles Dickens' Great Expectations to Harper Lee's To Kill a Mockingbird.

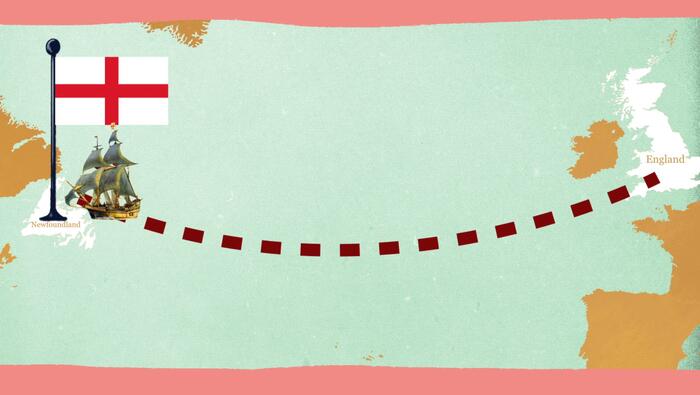
Newtown: A Crushing Defeat for the Iroquois
The Revolutionary War was never a simple story of Patriot vs Redcoat. Older nations with far deeper American roots were also caught up in the war. To secure their future, the nations of the Iroquois Confederacy had to choose a side – and in many ways, their long term fate was decided on the day of the Battle of Newtown.
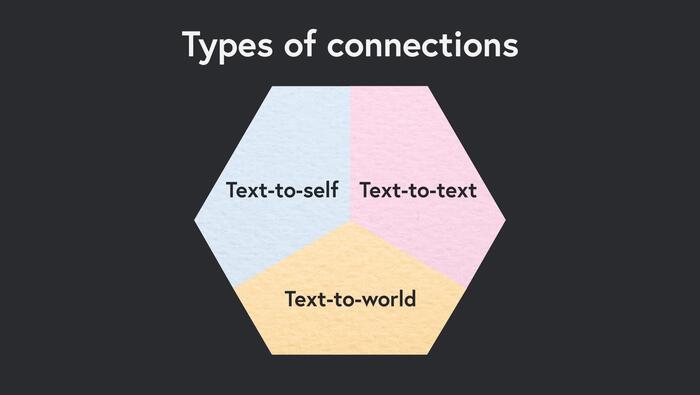
Making Connections Within the Text
One of the primary joys of reading is seeing yourself in a character, or seeing world events mirrored in the plot of a book. This is called making connections with texts and it not only enhances enjoyment, it also enhances understanding and your ability as a reader.

Feminism
This is a timeline of events in the feminist movement beginning from 1399 to the present day, including the Seneca Falls convention, the suffrage movement and the activism of Malala Yousafzai. Feminism has been a powerful movement throughout history, advocating for equal rights and opportunities for woman.
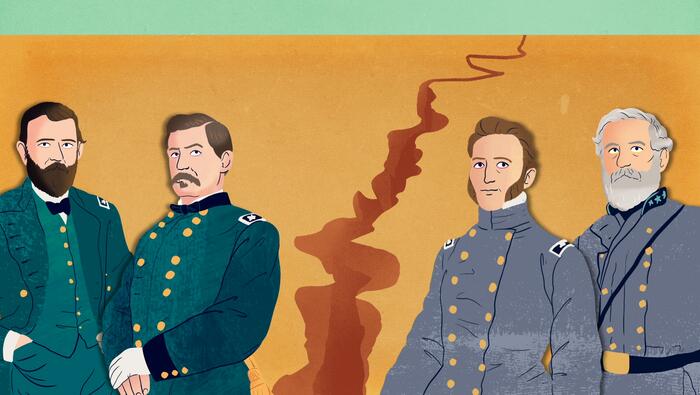
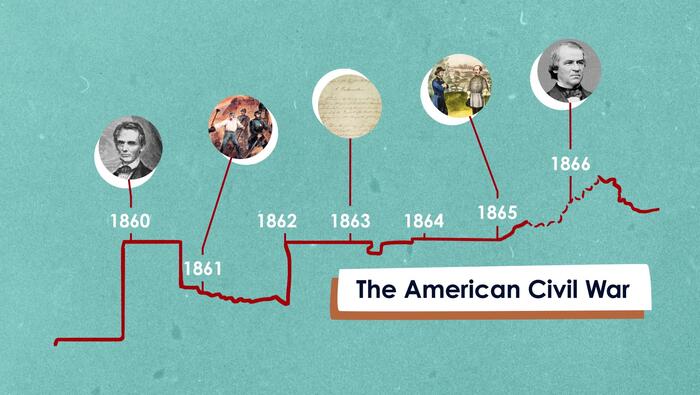
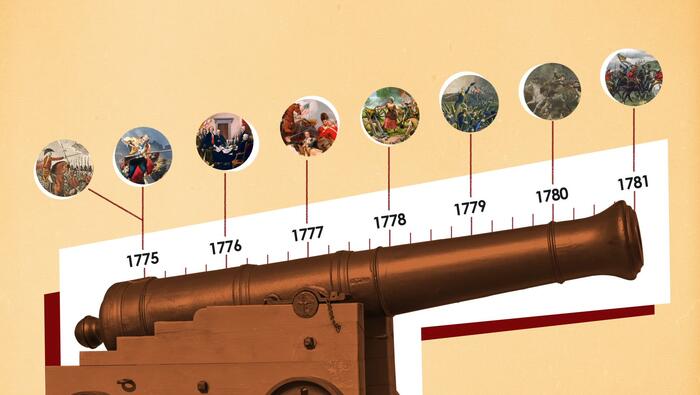
Leaders of the Civil War
The U.S. Civil War pitted friend against friend, neighbor against neighbor, in a bitter fight for the future of the nation. It also drove the country’s leaders apart. Their struggles are embodied by six men whose fates reflected the nation's continuing struggle for unity and progress.

Enslaved African Americans in the Revolution
At the time of the American Revolution, enslaved Africans made up a fifth of the population of the Thirteen Colonies. Though they were initially barred from taking part in the war, eventually thousands did. But what part did they play and what legacy did they leave?

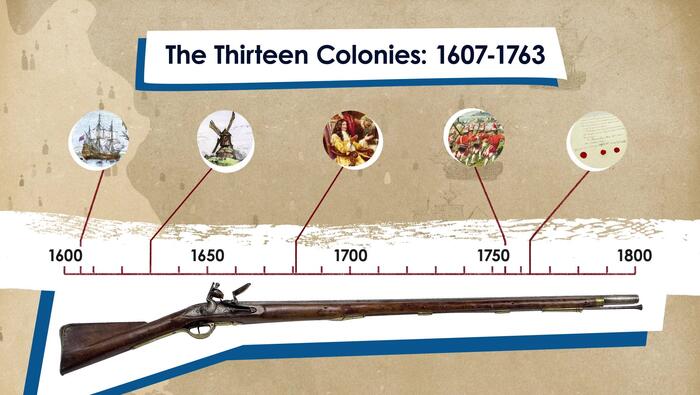
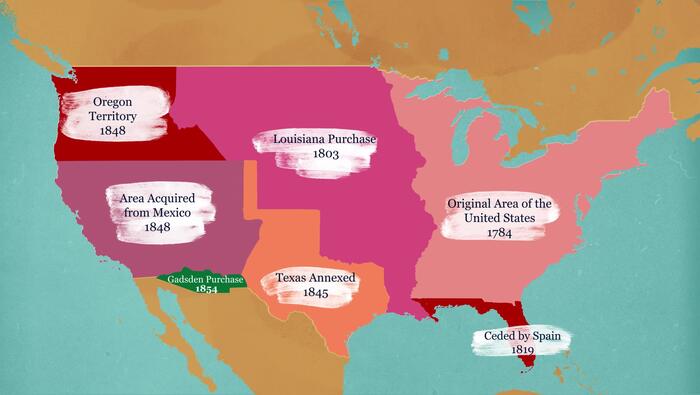
Europe and North America: 1620-1763
The period from 1620 to 1763 was a pivotal era that defined the relationship between Europe and North America. In this timeline video, learn how events in Europe influenced the colonization of North America and eventually solidified Great Britain’s hold on the Thirteen Colonies.

Catherine The Great
This Rebel girl overthrew her emperor husband to become Russia’s longest-reigning female ruler. And put her country on the map as one of the greatest nations in Europe. We explore who Catherine the Great was.
Based on the best-selling book series 'Goodnight Stories for Rebel Girls'.

Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte proved himself as a young army officer in the French Revolution. He soon became the Emperor of France, and in just eight years, conquered nearly all of Europe. However, he suffered a disastrous defeat invading Russia in 1812 and only a few years later, he finally met his match at the Battle of Waterloo and was sent into exile permanently where he died in 1821.
Independent India
Independent India emerged from British colonial rule which began with the East India Company in 1757. Mahatma Gandhi's peaceful protests catalyzed the independence movement in the 1920s. Post-World War II, divergent aspirations led to the 1947 partition into Hindu-majority India and Muslim-majority Pakistan, triggering massive migrations and significant violence.

Exploring the World
This is a timeline of the events in the history of the Age of Exploration from the early 1400s to 1521. During the 15th and 16th centuries, European explorers set sail to discover new lands, great riches and exotic goods, leading to the discovery of trade routes across the world and the first circumnavigation of the globe.

Michelle Obama
This Rebel Girl is a fierce champion of young women, who held one of the highest positions in public office of any African-American woman before her - as First Lady of the United States. We explore who Michelle Obama is.
Based on the bestselling books 'Goodnight Stories for Rebel Girls'.

Jane Austen
This Rebel Girl loved writing novels about women and marriage, society and manners, at a time when female authors were thoroughly disapproved of. And went on to become a literary superstar. We explore who Jane Austen was.
Based on the bestselling books 'Goodnight Stories for Rebel Girls'.

Beatrix Potter
This Rebel Girl captured our imaginations with her much-loved tales. An English writer who took matters into her own hands when no one would publish her stories,
And went on to become one of the world's bestselling children’s authors. We explore who Beatrix Potter was.
Based on the best-selling book series 'Goodnight Stories for Rebel Girls'.

Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
This Rebel Girl wanted the world to read stories that were a true reflection of life in Nigeria. So she wrote her own stories about Africa which inspired a new generation of readers around the world. We explore who Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie is.
Based on the best-selling book series 'Goodnight Stories for Rebel Girls'.

Grace Hopper
This Rebel Girl wanted to know what made things tick.
She turned a fascination with puzzles into a career in computer programming: then sailed into the history books as the oldest commissioned officer in the U.S. Navy. We explore who Grace Hopper was.
Based on the best-selling book series 'Goodnight Stories for Rebel Girls'.

Queen Elizabeth I
This Rebel Girl never expected to be queen of England and Ireland. She came to the throne when she was just 25 years old; And ruled over one of the greatest periods in English history. We explore who Queen Elizabeth I was.
Based on the best-selling book series 'Goodnight Stories for Rebel Girls'.